For the past half-dozen years or so, off-site manufacturers of components and modules have sprung up in response to growing demand for commercial prefabrication and modular construction. Most companies chasing this business read from the same song sheet when they describe their advantages over conventional in-field construction: lower building costs, better quality control, faster and more reliable construction scheduling, less material waste, safer working conditions.
A 2019 McKinsey & Co. report projected that modular could account for $130 billion in new real estate construction in the U.S. and Europe by 2030, driven by promises of 20% reductions in construction costs and far speedier building.
A 2020 Dodge Data & Analytics report, based on polling more than 600 AEC and manufacturing firms, found 93% of respondents citing improved productivity benefits from modular construction, and 89% citing productivity benefits from prefabrication. More than three-fifths of those polled expect to be deploying 3D modules and full volumetric construction for at least 10% of their projects within the next three years; 21% of respondents said they’d be using modular construction on more than half of their projects by then.
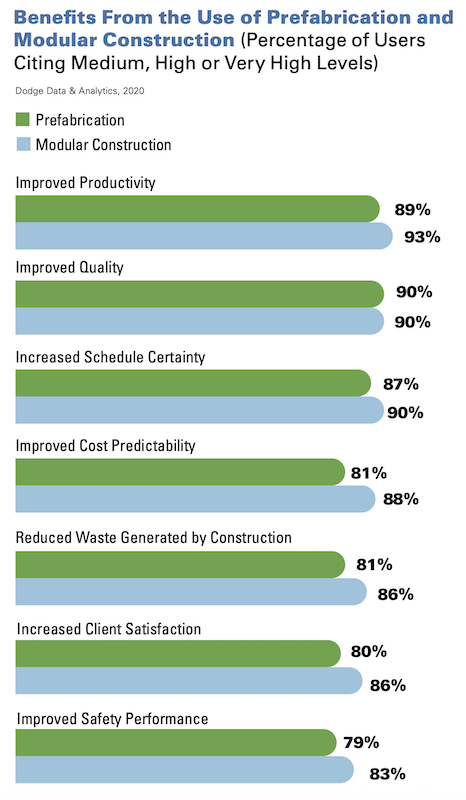
A 2020 poll of more than 600 AEC and manufacturing companies found almost unanimous consent about the benefits of modular manufacturing and prefabrication. Source and image: Dodge Data & Analytics
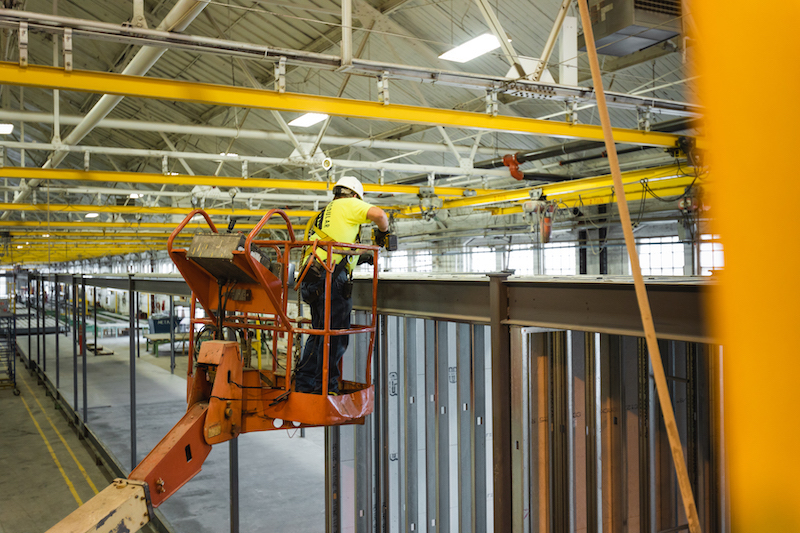
The synergies between construction and manufacturing have been apparent for a while. In 2014, the electricals contractor Faith Technologies launched Excellerate Manufacturing, which makes electrical components and assemblies. Since then, Excellerate has expanded to four facilities—in Appleton, Milwaukee, and Neenah, Wis., and Olathe, Kan.—with more than 600,000 sf of production space.

Since launching Excellerate Manufacturing in 2014, Faith Technologies has expanded this division to four faciliites, including a plant in Neenah, Wis. (above), and Olathe, Kan. (below). Images: Faith Technologies
Offsite manufacturers have also had ups and downs, false starts and second acts. In 2016, Full Stack Modular emerged, Phoenix-like, from the acquired assets of FC Modular, and has been focusing on building modules for mid- and high-rise housing from its 100,000-sf factory in Brooklyn. N.Y.
Last September, the design and construction firm Skender decided to close its 18-month-old modular-focused production spinoff Skender Manufacturing after lenders reportedly got cold feet because of the coronavirus pandemic’s economic impact, especially on the multifamily sector that Skender Manufacturing was targeting.
ALSO SEE: The epic rise of industrialized construction
Katerra made an even bigger splash when it debuted in 2015, and subsequently expanded aggressively through acquisitions and new production facilities. Billing itself as a technology company, Katerra was all about process improvements, said its executives. But Katerra has also experienced growth pains. In December, it was widely reported that the company required a $200 million bailout from Soft Bank Group to avoid bankruptcy. Soft Bank’s Vision Fund had already pumped $2 billion into the manufacturer, and the Japanese firm is now Katerra’s majority owner.
PUTTING REAL ESTATE DEVELOPERS ‘IN THE DRIVER’S SEAT’
Such setbacks have not diminished the reasons why prefabrication and modular construction remain attractive to developers and their AEC partners. Nor have they deterred new businesses from confidently entering the field with what they assert is a better mousetrap.
“How is it that construction, the largest industry at $13 trillion globally and $1.8 trillion domestically, still lags every other sector in productivity, with virtually every project late and over budget,” asks Ayall Schanzer, Chief Strategy Officer for iBUILT, a New York-based design-build-operate company that last November officially launched into the off-site manufacturing arena with $150 million in signed deals and another $600 million in negotiation, a number that has since risen to over $1 billion, says Schanzer.
iBUILT had been in the works since 2017-18, when the investment group behind its formation (whose constituents Schanzer declined to name) began assembling the pieces needed, first by acquiring Deluxe Modular, a Berwick, Pa.-based modular manufacturer founded in 1965, whose 24-acre campus currently includes three factories with a combined two million sf of annual production capacity. The next step was hiring software engineers who would devise programs that allow iBUILT to offer developers end-to-end solutions driven by technology and prefabrication.
(Earlier this month, iBUILT hired Gonzalo Gonzalez as its chief manufacturing officer. Gonzalez had been Tesla’s senior director of manufacturing and engineering.)
RELIEVING RISK OF OFFSITE CONSTRUCTION

iBUILT reduces developers' risks by offering an end-to-end solution that includes design, procurement, manfacturing, and construction management. Image: Courtesy iBUILT
iBUILT’s marketing tagline is “By Developers. For Developers.” Its business model is designed to give developers and owners greater control over their projects, with less risk.
Schanzer—who previously was president and CEO of Greiner-Maltz, a real estate brokerage—tells BD+C that iBUILT “incorporates input, throughout, and output” with services that include design, procurement, manufacturing, and construction management. iBUILT also delivers a digital twin of the project, embedded into its BIM models, that gives developers greater sway over the building’s operational costs.
iBUILT’s process begins with Fast Track, a software package that, for $25,000, delivers 70% of a project’s design with plans within 30 days. Schanzer insists that Fast Track’s delivery compares favorably to the 90-120 days developers normally wait for design plans that can cost anywhere from $100,000 to $500,000.
If a client decides to move forward on a project, iBUILT will commit to a finished price and delivery date. “Developers will know precisely, to the hinge, the cost,” says Schanzer. Working from its kit-of-parts catalog, iBUILT promises never to initiate a change order.
iBUILT’s website makes the familiar claims that its process lowers construction costs by 20%, speeds completions by 50%, and lowers operating costs by 70%. The company, with 80 employees, uses a combination of its own crews and subcontractors to assemble its modules on site, and can build as high as 35 stories using high-strength steel superstructures.
To meet the needs of clients concerned about their projects’ environmental impacts, iBUILT offers Smart Structures, a trademarked process that leverages automation and technology to adhere to stringent codes. Smart Structures are built with sustainable materials to standards that exceed LEED and, if requested, can achieve Passive House insulation values. The company even has its own designation, iBUILT Green, which Schanzer suggests could be a selling point for developers down the road.
LOOKING BEYOND HOUSING FOR OFFSITE CONSTRUCTION
iBUILT’s proprietary digital twin AI software is embedded into each of its BIM models. This allows clients to control and manage ongoing building operations, reducing maintenance costs by 70%, while providing preventive forewarnings to avert catastrophic breakdowns, and benefiting from reduced insurance premiums. Image: iBUILT
Over the decades, Deluxe Modular had supplied products for several building sectors including healthcare, hospitality, education, recreation, and military, although most of its production was for multifamily and student housing. The website ForConstructionPros.com identified two of iBUILT’s projects that are in the works: a condo project in Brooklyn, N.Y., that will leverage smart building technology; and a 100-unit affordable housing development in Baltimore that iBUILT is building for the developer I&G Group.
Schanzer, though, envisions a broader canvas for iBUILT, whose goal is to double its production capacity by year’s end, at which point one of iBUILT’s factories will be fully automated. He can also see the eventual opening of factories in other regions of the country.
ALSO SEE: Meet the masters of offsite construction
A year from now, he predicts, “we are going to be a dominant force in the market, with several visible projects underway.” Clients will be able to access design options, optimized by budget and land availability, and select products from iBUILT’s catalog. “This will be a fully integrated digital program that will talk to our ERP system, order products, schedule design and manufacturing,” he says.
When asked what pitfalls iBUILT needs to avoid, Schanzer responds “calibrating our growth. We’re going to expand prudently and organically.” But he’s not ruling out mergers or acquisitions under the right circumstances.
Related Stories
K-12 Schools | Apr 30, 2024
Fully electric Oregon elementary school aims for net-zero carbon and resiliency
The River Grove Elementary School in Oregon was designed for net-zero carbon and resiliency to seismic events, storms, and wildfire. The roughly 82,000-sf school in a Portland suburb will feature a microgrid—a small-scale power grid that operates independently from the area’s electric grid.
AEC Tech | Apr 30, 2024
Lack of organizational readiness is biggest hurdle to artificial intelligence adoption
Managers of companies in the industrial sector, including construction, have bought the hype of artificial intelligence (AI) as a transformative technology, but their organizations are not ready to realize its promise, according to research from IFS, a global cloud enterprise software company. An IFS survey of 1,700 senior decision-makers found that 84% of executives anticipate massive organizational benefits from AI.
Codes and Standards | Apr 30, 2024
Updated document details methods of testing fenestration for exterior walls
The Fenestration and Glazing Industry Alliance (FGIA) updated a document serving a recommended practice for determining test methodology for laboratory and field testing of exterior wall systems. The document pertains to products covered by an AAMA standard such as curtain walls, storefronts, window walls, and sloped glazing. AAMA 501-24, Methods of Test for Exterior Walls was last updated in 2015.
MFPRO+ News | Apr 29, 2024
World’s largest 3D printer could create entire neighborhoods
The University of Maine recently unveiled the world’s largest 3D printer said to be able to create entire neighborhoods. The machine is four times larger than a preceding model that was first tested in 2019. The older model was used to create a 600 sf single-family home made of recyclable wood fiber and bio-resin materials.
K-12 Schools | Apr 29, 2024
Tomorrow's classrooms: Designing schools for the digital age
In a world where technology’s rapid pace has reshaped how we live, work, and communicate, it should be no surprise that it’s also changing the PreK-12 education landscape.
Adaptive Reuse | Apr 29, 2024
6 characteristics of a successful adaptive reuse conversion
In the continuous battle against housing shortages and the surplus of vacant buildings, developers are turning their attention to the viability of adaptive reuse for their properties.
AEC Innovators | Apr 26, 2024
National Institute of Building Sciences announces Building Innovation 2024 schedule
The National Institute of Building Sciences is hosting its annual Building Innovation conference, May 22-24 at the Capital Hilton in Washington, D.C. BI2024 brings together everyone who impacts the built environment: government agencies, contractors, the private sector, architects, scientists, and more.
Mass Timber | Apr 25, 2024
Bjarke Ingels Group designs a mass timber cube structure for the University of Kansas
Bjarke Ingels Group (BIG) and executive architect BNIM have unveiled their design for a new mass timber cube structure called the Makers’ KUbe for the University of Kansas School of Architecture & Design. A six-story, 50,000-sf building for learning and collaboration, the light-filled KUbe will house studio and teaching space, 3D-printing and robotic labs, and a ground-level cafe, all organized around a central core.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Apr 25, 2024
How pools can positively affect communities
Clark Nexsen senior architects Jennifer Heintz and Dorothea Schulz discuss how pools can create jobs, break down barriers, and create opportunities within communities.
Senior Living Design | Apr 24, 2024
Nation's largest Passive House senior living facility completed in Portland, Ore.
Construction of Parkview, a high-rise expansion of a Continuing Care Retirement Community (CCRC) in Portland, Ore., completed recently. The senior living facility is touted as the largest Passive House structure on the West Coast, and the largest Passive House senior living building in the country.

















