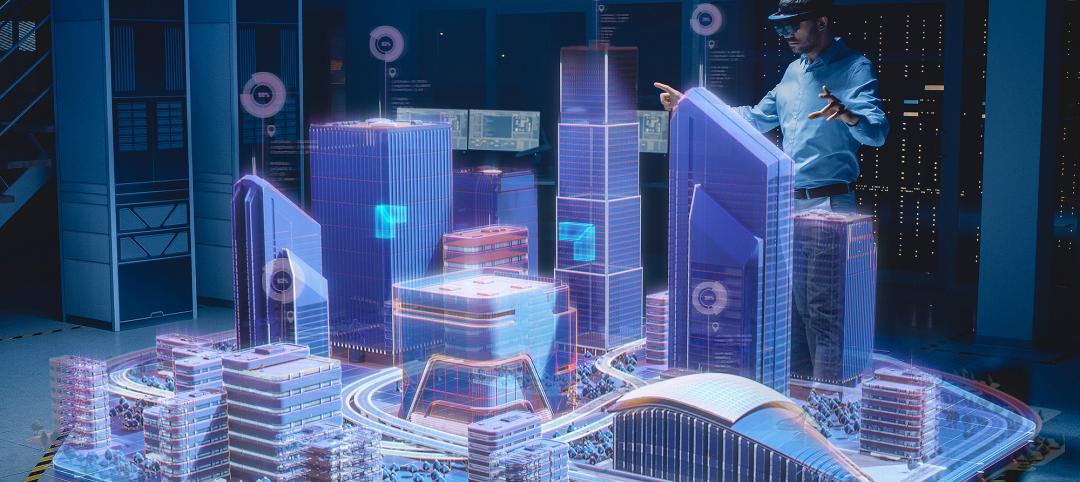
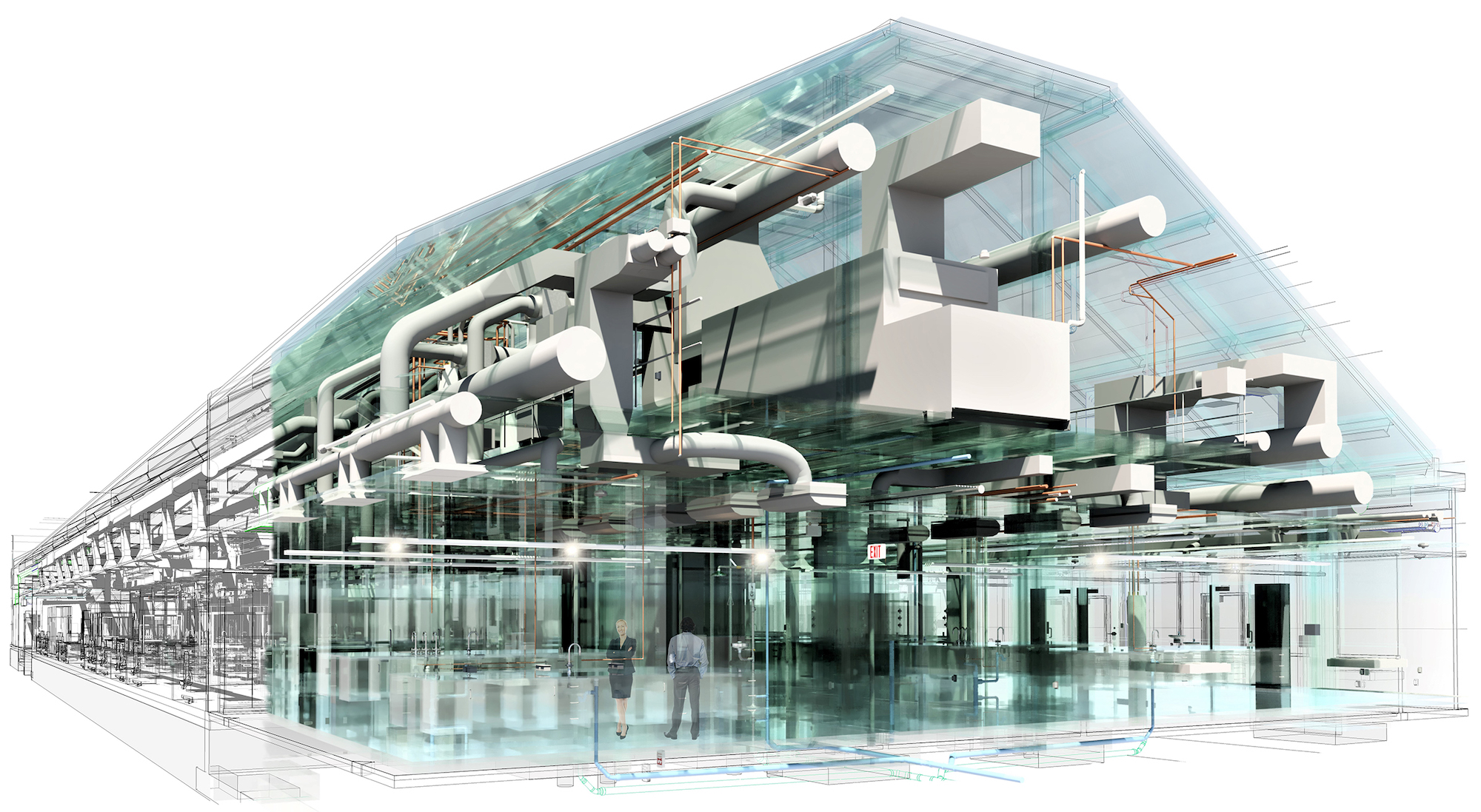
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has become a standard practice in the construction industry, revolutionizing the design and construction phases of buildings. However, building owners are now realizing the potential of extending the use of BIM beyond construction into facility management. This has led to the emergence of the Digital Twin concept, which leverages the as-built BIM model as an exact digital replica of the built structure. By collecting data through sensors and tracking systems, the Digital Twin enables facility owners to analyze and forecast facility repairs and maintenance over the building's lifespan.
Aligning the BIM model with the owner’s asset management system is the crucial first step in creating a Digital Twin. Designers can ensure that the Digital Twin meets the owner’s long-term needs by effectively communicating objectives, addressing client concerns, and engaging the facilities management team. Considerations such as aligning the asset registry with the owner’s Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS), establishing BIM Level of Development (LOD) by system or element, and incorporating critical asset data for long-term operations are essential for a successful Digital Twin implementation. Collaboration with vendors and manufacturers who provide accessible BIM data further enhances the integration and management of the Digital Twin.
By following these guidelines, organizations can harness the power of Digital Twins to optimize facility management, maintenance planning, and decision-making throughout the building’s lifecycle.
Talk with the Owner
When introducing the concept of an as-built BIM to clients, designers should communicate the objectives and expectations of the Digital Twin project. By addressing any concerns the client may have, designers can align long-term objectives and ensure that the Digital Twin meets the owner's needs. Designers should also engage the facilities management team in project discussions. You should discuss the following considerations.
- Asset Registry Alignment with the Owner's CMMS: The asset registry, which catalogs the equipment and components within the Digital Twin, should be aligned with the owner's CMMS. This integration enables the seamless transfer of asset information, such as maintenance schedules, historical data, and work orders, facilitating efficient maintenance planning and execution.
- BIM LOD by System or Element: The BIM model's LOD, which defines the level of detail and accuracy, should be established by the system or element in the Digital Twin. This ensures that critical systems or elements, such as HVAC, electrical, or structural components, are represented with the necessary level of fidelity for accurate simulation and analysis.
- Critical Asset Data for Long-Term Operations: Identifying and incorporating the specific asset data that the owner will utilize for long-term operations is crucial. This can include information such as equipment specifications, maintenance history, warranties, energy consumption, and performance metrics. By integrating this data into the Digital Twin, owners can make informed decisions regarding maintenance strategies, energy optimization, and asset lifecycle planning.
Develop Your Asset Registry
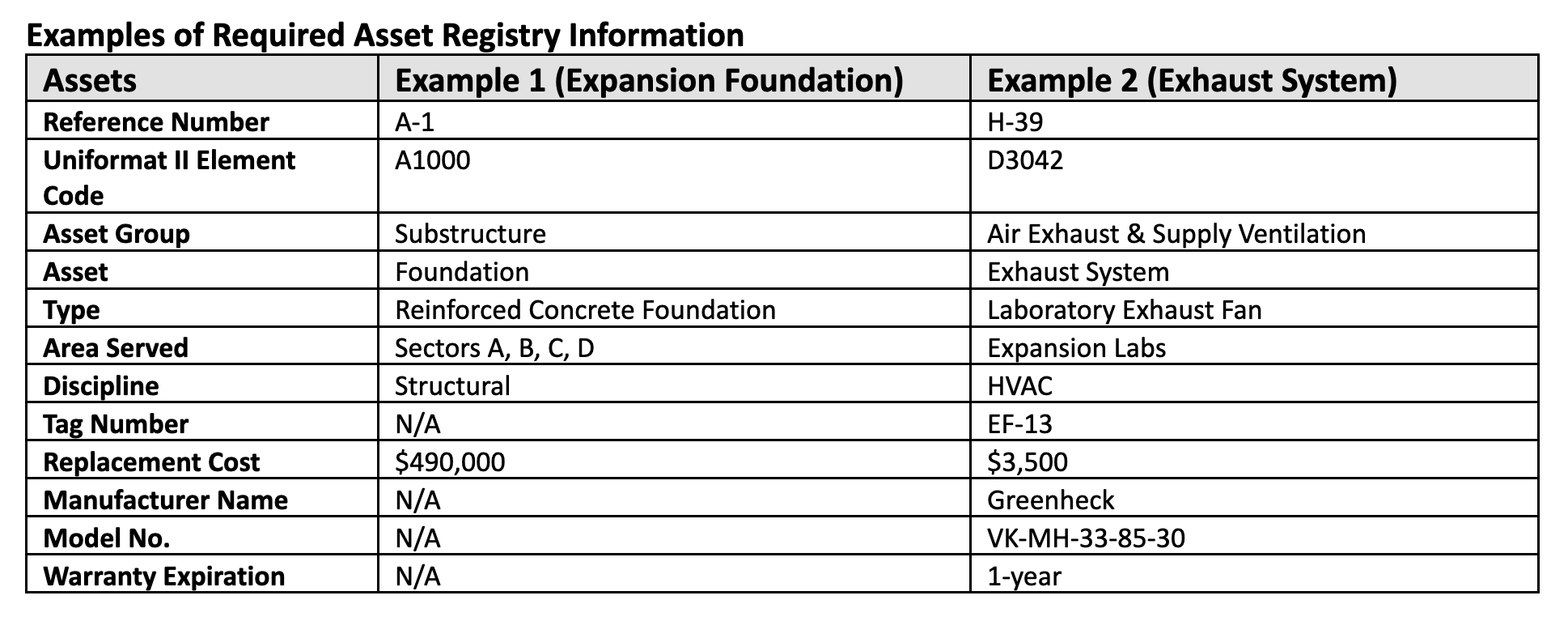
The integration between BIM models and asset management platforms is often lacking, resulting in misaligned asset data and CMMS data. To address this issue, designers who possess expertise in BIM can play a crucial role during the design phase by aligning the asset registry and BIM model. During the design phase, or around 90% design, an asset registry should be created to align with different building equipment, components, or systems. In these two examples, the owner requested that each asset within the BIM model include the following information at a minimum.
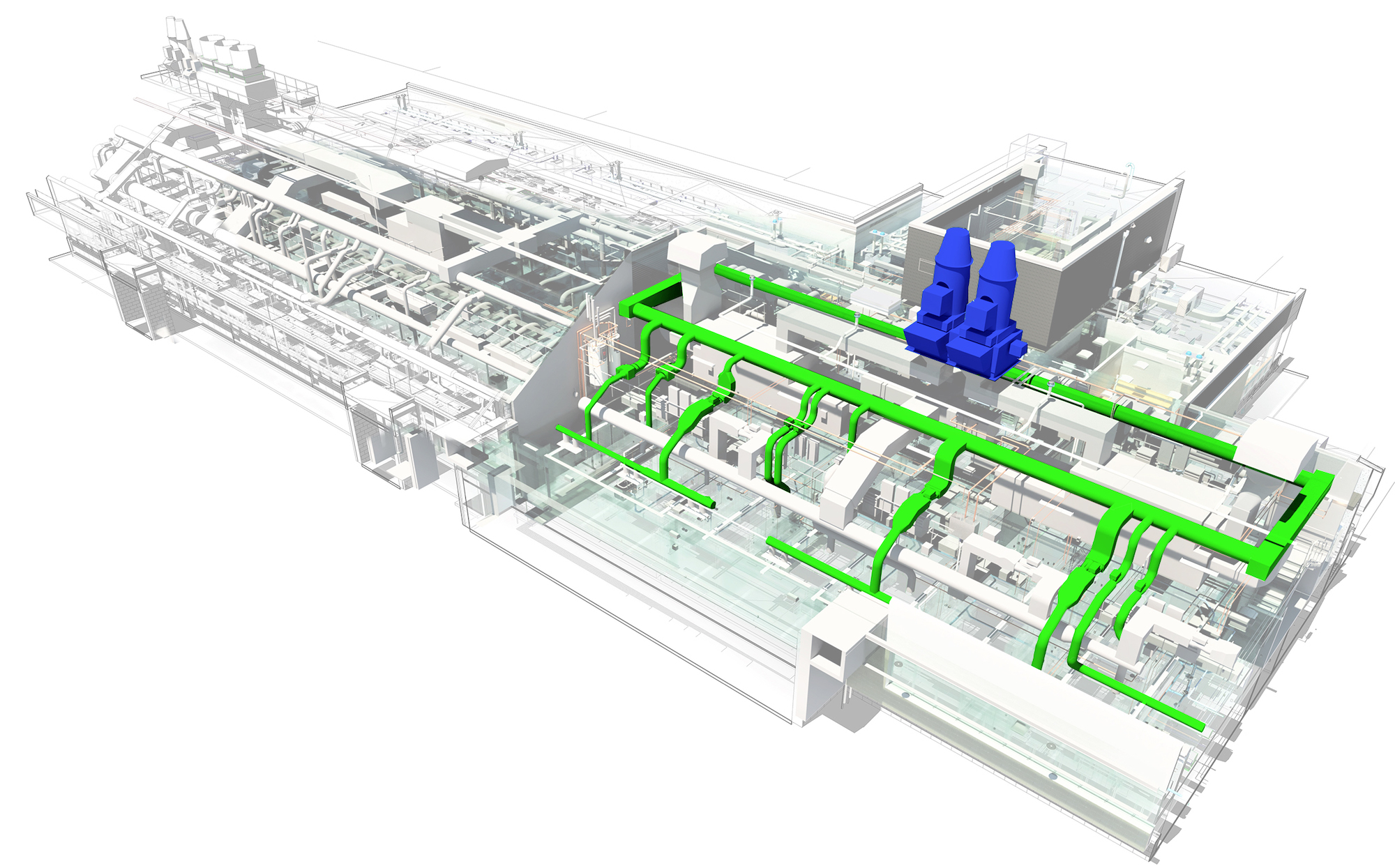
Single vs Grouping Assets
To provide a clear understanding of the asset registry and the BIM model, let’s examine how they work together. In the asset registry, you can find a description of the same asset that is also present in the BIM model. It allows for easy cross-referencing and ensures consistency between the two.
It’s important to note that certain assets are more suitable as individual components, while others are better organized as part of an entire building system. For example, an air handler is typically considered an individual asset, whereas a laboratory exhaust system is better classified as a grouped system. By considering this distinction, you can optimize the organization and management of assets within the registry and BIM model. This captures the complexity of the building systems while maintaining clarity and coherence.
Creating a Digital Twin requires a shift in the designer’s approach to BIM. Designers need to adopt a long-term perspective that extends beyond construction and incorporates facility management workflows. Manufacturers have recognized the importance of BIM and have made efforts to make their data easily accessible. In some cases, they have developed software that seamlessly integrates with industry-wide BIM programs.
Establishing digital connections with vendors allows facility managers to utilize the data flow into BIM for effective management decisions. During the submittal process, it is possible to have a vendor provide an accurate BIM component or system that can be incorporated into the BIM model. This limits the effort of the design team to transfer the information from contractor submittals into the model.
Application and Lessons Learned
To meet the demands of a growing population in the DC area, WSSC Water embarked on a project to expand their environmental laboratory facility in Silver Spring, Maryland. WSSC Water aimed to increase operational and analytical efficiency and achieve LEED Silver Certification for the new facility. This project provides opportunities for WSSC Water to reimagine their asset registry development process by leveraging advancements in machine learning, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and data collection methods in the future.
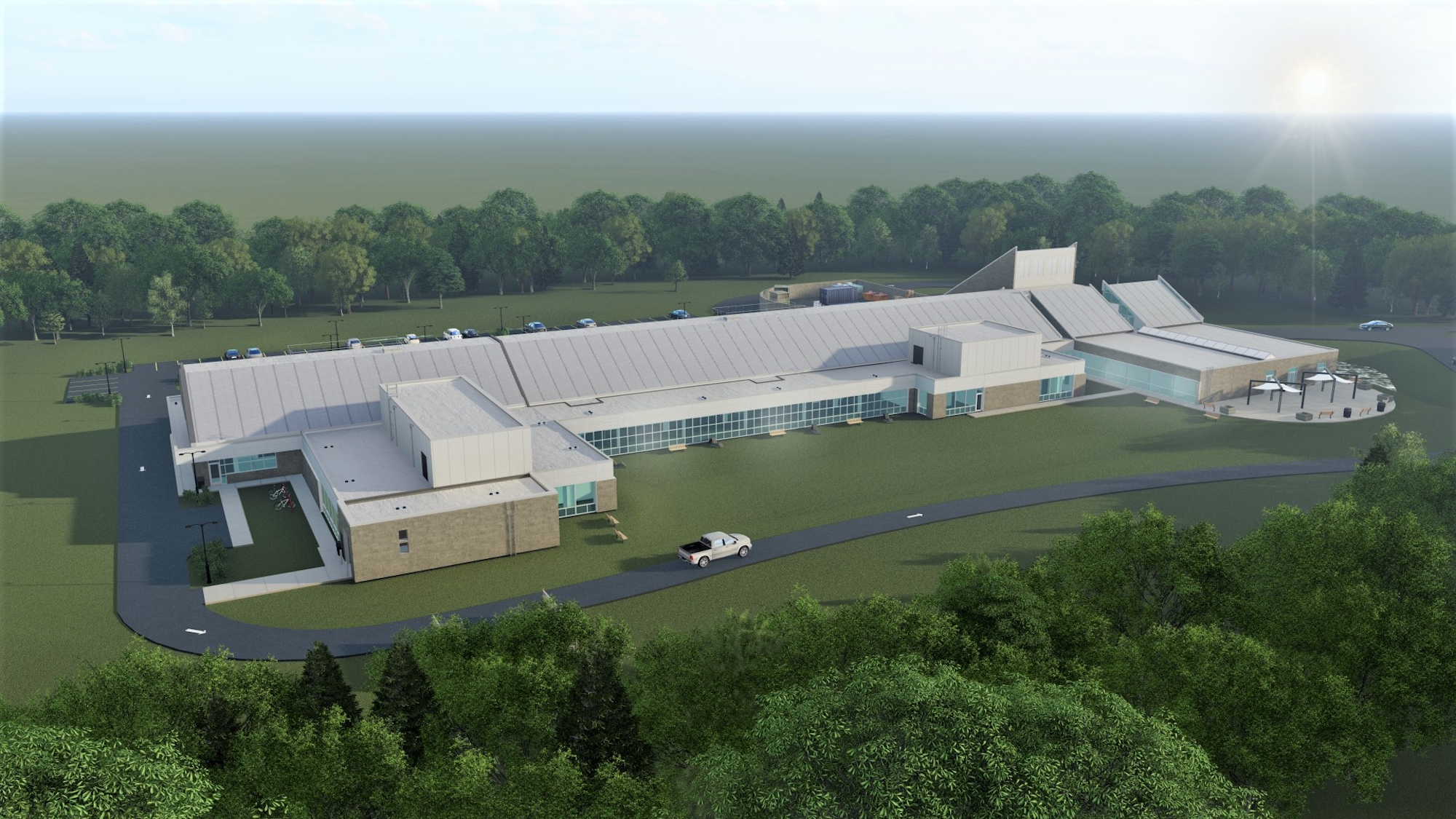

WSSC Water collaborated with the architect to develop a BIM model during the design phase. This model served as a repository of all assets anticipated for construction. During ongoing construction administration, real-time as-built data provided by manufacturers through construction submittals and requests for information are integrated into the BIM model.
Each asset was linked to product data, Uniformat codes, material properties, and manufacturer information that will be handed over to WSSC Water upon construction completion. With a digital as-built model, WSSC Water’s facilities management team can take the next step of integrating live-stream information and establishing a Digital Twin of the new laboratory.
Several challenges or opportunities were discovered during the as-built development phase of work.
Creating consistent parameters for each asset across disciplines. As the team started to assign parameters for each discipline model, we discovered that the method of creating parameters needed to be more consistent. For consistency across discipline models, we established a format and assigned a single BIM coordinator to create these parameters for quality assurance. Information such as Uniformat code and manufacturer name are custom parameters applicable to all assets in every discipline. Establishing a project-wide method for assigning these common parameters across disciplines early in the design phase will pay off later when specific asset information is needed and can be easily filtered.
Managing design changes during construction administration. During construction, it is common for product substitutions to be made and designs to be altered. Tracking these changes in the as-built BIM model can be tedious and time-consuming. These changes may also require the complete removal of a basis-of-design system with the new product being proposed. During design, WSSC Water selected demountable partitions to allow for future re-configuration of offices and laboratories.
As a basis of design, we worked with a manufacturer that provided custom geometry imported into BIM. The asset data embedded within the geometry met and exceeded client expectations. However, during construction, the contractor selected a similar product from a different manufacturer whose BIM geometry was not as robust as the basis of design. The best solution is to require manufacturers to provide updated geometry in the specifications to support the as-built model. Whoever is managing the model should anticipate spending time changing out the basis of design to match the constructed assets.
Related Stories
AEC Innovators | Apr 26, 2024
National Institute of Building Sciences announces Building Innovation 2024 schedule
The National Institute of Building Sciences is hosting its annual Building Innovation conference, May 22-24 at the Capital Hilton in Washington, D.C. BI2024 brings together everyone who impacts the built environment: government agencies, contractors, the private sector, architects, scientists, and more.
AEC Tech | Mar 9, 2024
9 steps for implementing digital transformation in your AEC business
Regardless of a businesses size and type, digital solutions like workflow automation software, AI-based analytics, and integrations can significantly enhance efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.
AEC Tech | Feb 28, 2024
How to harness LIDAR and BIM technology for precise building data, equipment needs
By following the Scan to Point Cloud + Point Cloud to BIM process, organizations can leverage the power of LIDAR and BIM technology at the same time. This optimizes the documentation of existing building conditions, functions, and equipment needs as a current condition and as a starting point for future physical plant expansion projects.
AEC Innovators | Feb 28, 2024
How Suffolk Construction identifies ConTech and PropTech startups for investment, adoption
Contractor giant Suffolk Construction has invested in 27 ConTech and PropTech companies since 2019 through its Suffolk Technologies venture capital firm. Parker Mundt, Suffolk Technologies’ Vice President–Platforms, recently spoke with Building Design+Construction about his company’s investment strategy.
AEC Tech | Jan 8, 2024
What's driving the surge of digital transformation in AEC today?
For centuries, the AEC industry has clung to traditional methods and legacy processes—seated patterns that have bred resistance to change. This has made the adoption of new technologies a slow and hesitant process.
Digital Twin | Jul 17, 2023
Unlocking the power of digital twins: Maximizing success with OKRs
To effectively capitalize on digital twin technology, owners can align their efforts using objectives and key results (OKRs).
Digital Twin | May 8, 2023
What AEC professionals should know about digital twins
A growing number of AEC firms and building owners are finding value in implementing digital twins to unify design, construction, and operational data.
Digital Twin | Nov 21, 2022
An inside look at the airport industry's plan to develop a digital twin guidebook
Zoë Fisher, AIA explores how design strategies are changing the way we deliver and design projects in the post-pandemic world.
Sponsored | Digital Twin | Jun 24, 2022
Pave the way for better business relationships with digital twins