When it comes to the building of the future, every material used in construction needs to pull its weight. For a building to become as sustainable, environmentally friendly, and as comfortable as possible, there can be no slackers on the materials front.
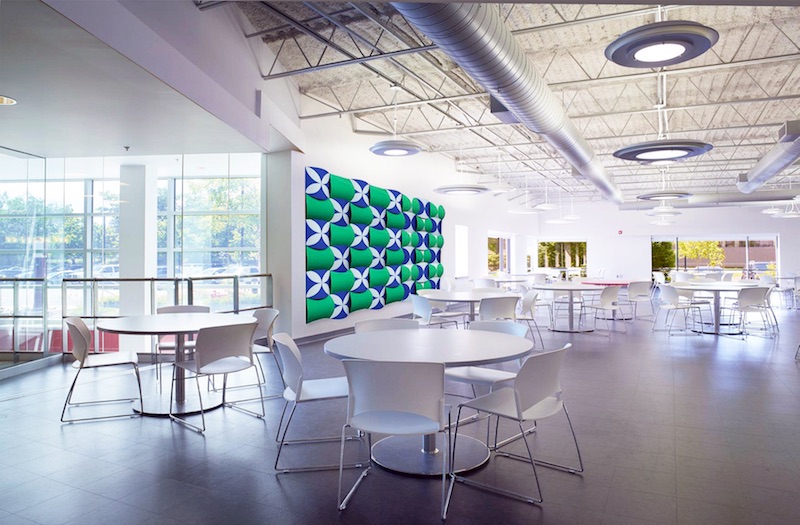
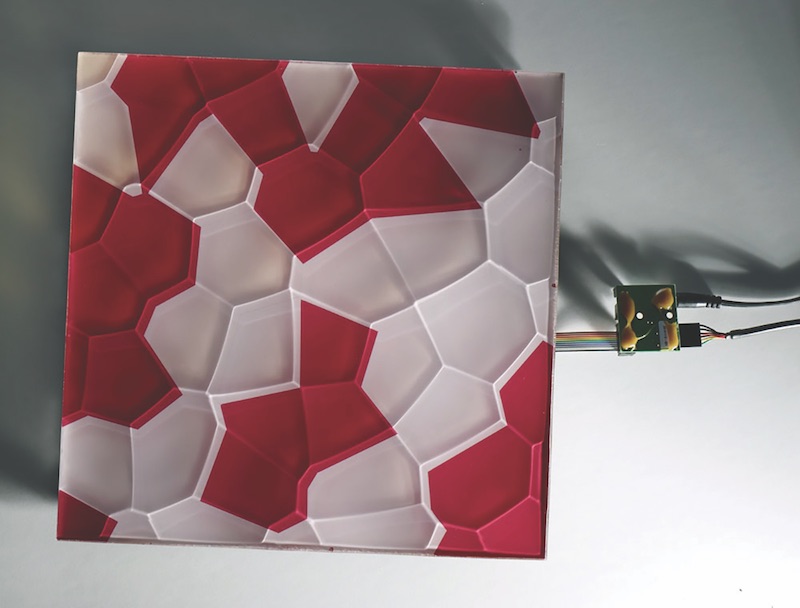
Take the newest offering from E Ink. Using the same E Ink bi-stable ink technology found in its current line of eReaders and wearables and integrating it with traditional architectural materials, E Ink Prism creates a new way for commercial spaces such as large hotel lobbies, office complexes, and airports to change the aesthetics of the space without resorting to a large LCD or LED screen—and the light pollution and higher energy demands that come with it.
E Ink Prism has a paint-like appearance and a wide-ranging compatibility with various materials and shapes that make it highly suitable for architectural applications. E Ink Prism comes in seven different colors—Voyage (dark blue), Daydream (cyan), Blush (red), Sprout (green), Zest (yellow), Harvest (brown) and Waltz (black)—and can be sized to be compatible with most configurations, patterns, and materials.
The film can be programmed to dynamically switch colors in nearly any pattern, shape, speed, and sequence. During these visual changes, E Ink Prism only requires ultra-low power and never requires the use of electrical outlets. The film does not provide any illumination and, as with paint, its visibility is based on ambient light.
 Courtesy of E Ink.
Courtesy of E Ink.
Recent developments are beginning to point to a much more utilitarian future for paint. Researchers at RMIT University, Melbourne, have developed a paint that can absorb water vapor and use solar energy to split it and generate hydrogen. Hydrogen, which is often referred to as the cleanest source of energy, can be used in fuel cells or in conventional combustion engines as an alternative to fossil fuels.
The paint contains synthetic molybdenum sulfide, a new material that acts as a semiconductor and catalyses the splitting of water atoms into hydrogen and oxygen, according to RMIT. All that is needed for the paint to produce fuel is solar energy and moist air.
Applied to a brick wall of a building, the paint instantly converts the wall into an energy-harvesting, fuel-production space. Areas with humid climates provide ideal applications for the paint. But its developers say the material can also be used in applications in very dry, hot climates near oceans. As the seawater is evaporated, the paint will absorb the vapor and produce fuel.
 Courtesy of RMIT University.
Courtesy of RMIT University.
Related Stories
75 Top Building Products | Apr 22, 2024
Enter today! BD+C's 75 Top Building Products for 2024
BD+C editors are now accepting submissions for the annual 75 Top Building Products awards. The winners will be featured in the November/December 2024 issue of Building Design+Construction.
AEC Tech | Feb 20, 2024
AI for construction: What kind of tool can artificial intelligence become for AEC teams?
Avoiding the hype and gathering good data are half the battle toward making artificial intelligence tools useful for performing design, operational, and jobsite tasks.
Sustainability | Nov 1, 2023
Researchers create building air leakage detection system using a camera in real time
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have developed a system that uses a camera to detect air leakage from buildings in real time.
Resiliency | Aug 7, 2023
Creative ways cities are seeking to beat urban heat gain
As temperatures in many areas hit record highs this summer, cities around the world are turning to creative solutions to cope with the heat. Here are several creative ways cities are seeking to beat urban heat gain.
AEC Innovators | Jun 15, 2023
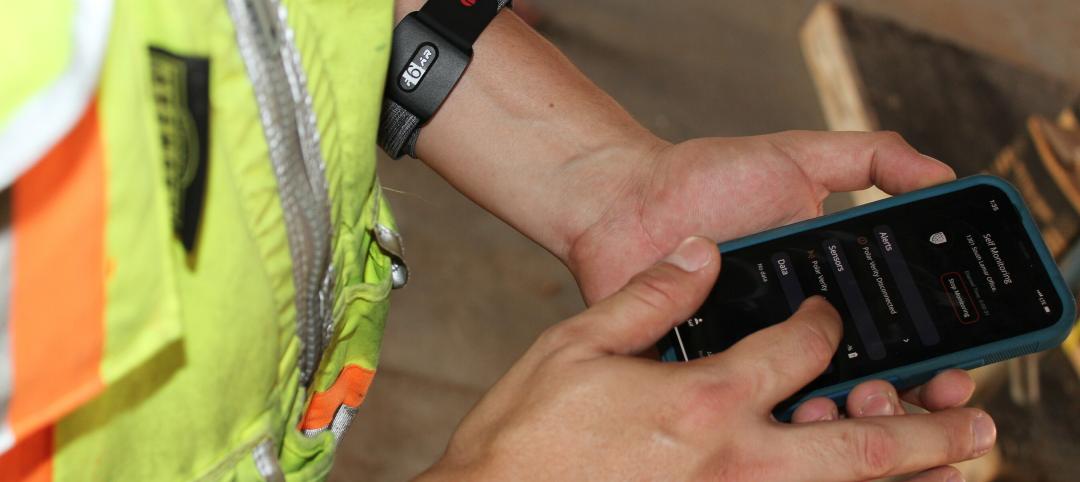
Rogers-O'Brien Construction pilots wearables to reduce heat-related injuries on jobsites
Rogers-O'Brien Construction (RO) has launched a pilot program utilizing SafeGuard, a safety-as-a-service platform for real-time health and safety risk assessment. Non-invasive wearables connected to SafeGuard continuously monitor personnel to prevent heat exhaustion on jobsites, reducing the risk of related injuries. RO is the first general contractor to pilot this program.
Office Buildings | May 15, 2023
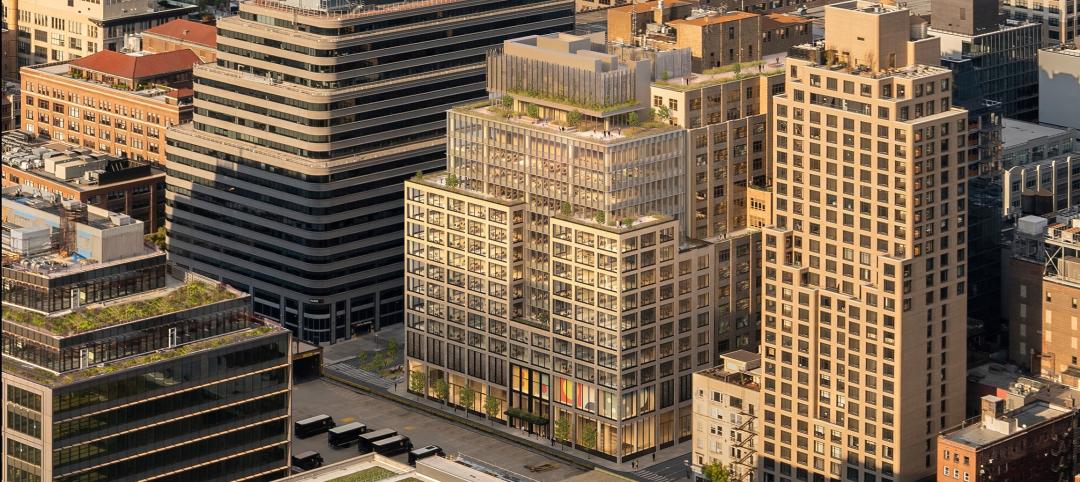
Sixteen-story office tower will use 40% less energy than an average NYC office building
This month marks the completion of a new 16-story office tower that is being promoted as New York City’s most sustainable office structure. That boast is backed by an innovative HVAC system that features geothermal wells, dedicated outdoor air system (DOAS) units, radiant heating and cooling, and a sophisticated control system to ensure that the elements work optimally together.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 27, 2023
BD+C's 2023 Design Innovation Report
Building Design+Construction’s Design Innovation Report presents projects, spaces, and initiatives—and the AEC professionals behind them—that push the boundaries of building design. This year, we feature four novel projects and one building science innovation.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
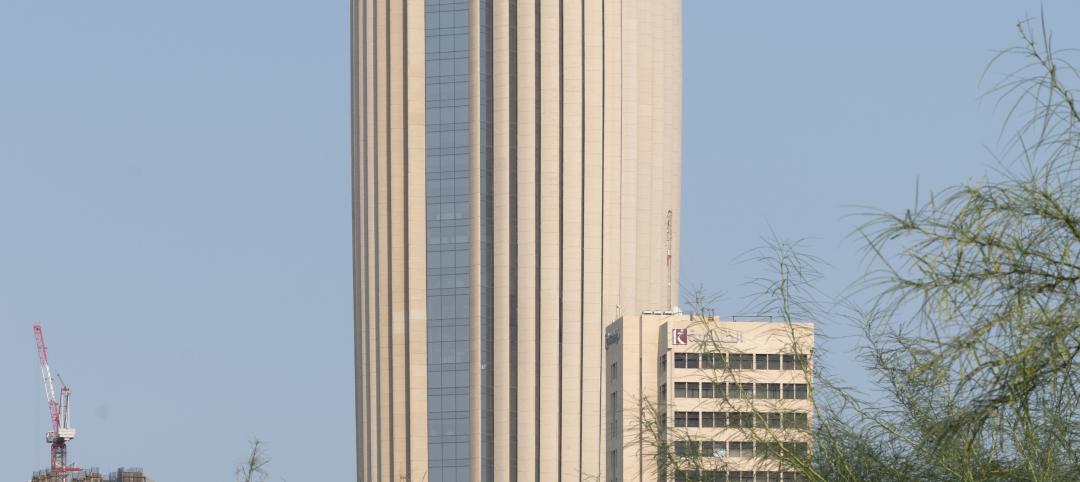
Reinforced concrete walls and fins stiffen and shade the National Bank of Kuwait skyscraper
When the National Bank of Kuwait first conceived its new headquarters more than a decade ago, it wanted to make a statement about passive design with a soaring tower that could withstand the extreme heat of Kuwait City, the country’s desert capital.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
HDR uses artificial intelligence tools to help design a vital health clinic in India
Architects from HDR worked pro bono with iKure, a technology-centric healthcare provider, to build a healthcare clinic in rural India.
3D Printing | Apr 11, 2023
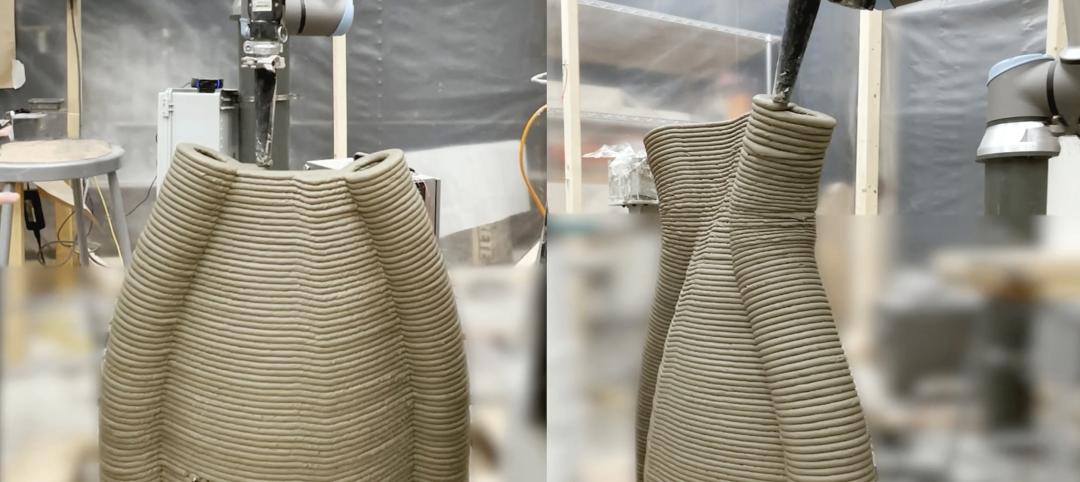
University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory unveils Shell Wall—a concrete wall that’s lightweight and freeform 3D printed
The University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory has unveiled a new product called Shell Wall—which the organization describes as the first lightweight, freeform 3D printed and structurally reinforced concrete wall. The innovative product leverages DART Laboratory’s research and development on the use of 3D-printing technology to build structures that require less concrete.

















