Lexicographers trace the old saying “waste not, want not” back to late 18th century England. It took us engineers a couple of centuries to catch on, but finally we’re embracing a very literal interpretation of that adage to tap into an abundant, secure and economical source of renewable energy for the next generation of green buildings. Even better, this energy is easily accessible, for it already flows through pipes right beneath our feet: wastewater.
Take a second to get past the yuck factor and then consider: As much as 40 to 50% of a building’s energy literally goes down the drain every day. When the water we heat for cooking, cleaning, bathing and washing our clothes, among other uses, enters a sewer system, it helps to heat the wastewater flowing through that system to an average temperature of 60-70 degrees F, thereby creating a stable, flowing geothermal source of energy that until now—in the U.S at least—we’ve been, well, wasting.
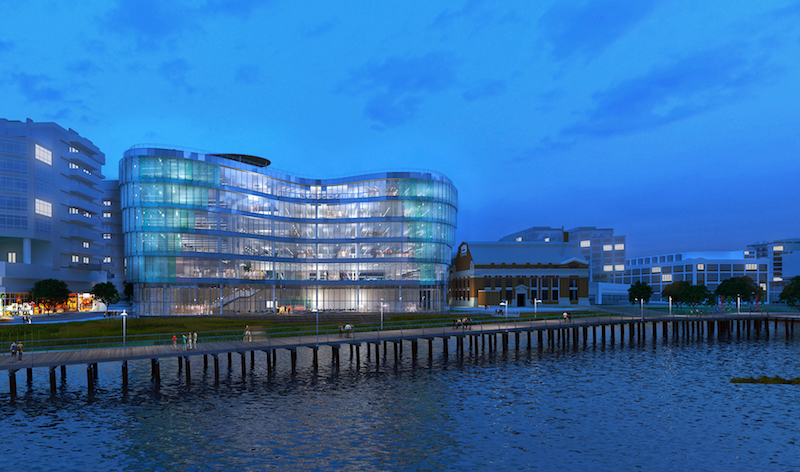
But what if we could recover some of that wasted energy, recycling it back into our buildings for heating in the winter and cooling in the summer? Well, we can and in 2018, we will be doing it in our nation’s capital at the DC Water’s new state-of-the-green-art headquarters on the banks of the Anacostia River in southeast Washington, DC.
SmithGroupJJR’s involvement in this project started with a design competition launched in 2014, when DC Water issued a Design-Build Request for Qualifications for a new headquarters building to relocate its administrative facilities from its overcrowded Blue Plains waste treatment facility.
DC Water was looking for their new headquarters to be, “DC Water’s most sustainable construction project ever and provide a visible connection to the community that DC Water serves.” To achieve this goal they challenged the design teams to “achieve the highest level of sustainability… including attainment of a LEED Platinum certification in furtherance of DC Water’s strategic goals and commitment to protecting the environment.”
From a field of three finalists, the Skanska + SmithGroupJJR Design-Build team was selected to design and construct the new 150,000 sq. ft. headquarters. To meet DC Water’s aggressive sustainability goals, our team knew we had to look not only at the most advanced technologies available in the US, but also at innovative technologies that were best in class around the world. We wanted, in short, to push the “platinum” envelope.
The Challenge—and Our Response
A major challenge at the outset was a requirement that the new office structure be built on top of the existing O Street Pumping Station and adjacent to the Historic Pumping Station – two facilities that receive and pump 45 million gallons of wastewater a day from the nation’s capital to the Blue Plains wastewater treatment plant. Obviously, shutting the pumping stations down was not an option. Overcoming this challenge required us to approach the problem not as an obstacle but an opportunity. Could we find a way to incorporate a historic, century-old infrastructure into the design as an asset to help leverage 21st century energy and water efficiency goals?
We found the answer by looking to the Old Country—Europe, which has been ahead of our curve in pioneering and deploying technologies to capture and re-use expended energy. This is technology that has been tested and proven across much of Europe, parts of Asia and, more recently, in Canada. However, due to the burdens of our regulatory system, it only recently received approval for use in the U.S. But it is comparatively simple and cost-effective technology whose time has come.
When we first briefed DC Water on the technology to turn wastewater into a renewable source of energy they immediately got it. Committed to sustainability, they were ready to consider new ideas and were excited about the possibilities – the kind of client that engineers like me dream of having.
Initial research by the Skanska + SmithGroupJJR team soon indicated that there were two types of technology in use around the world to do this: in-line systems with underground energy exchange piping systems, and off-line systems utilizing pumped wastewater and above ground heat exchangers.
The process is similar in both cases. Raw wastewater passes through a separator, which removes solid waste and sends it back to the sewer. The liquid waste then passes through a heat exchanger, which extracts its thermal energy to heat a separate stream of clean fluid. The heat-depleted wastewater returns to the sewer, while a heat pump distributes the clean fluid throughout a building in much the same way as a conventional boiler and radiator system works.
The difference is that in-line systems install exchangers on the invert side of the sewer pipes themselves, which requires pipes with a larger diameter than those found in most existing and older municipal sewer systems. In those systems – with Washington, DC being a case in point—a building’s wastewater is first collected in a well or pit before being pumped through a conventional heat exchanger equipped with a filtering system to separate solid and liquid wastes.
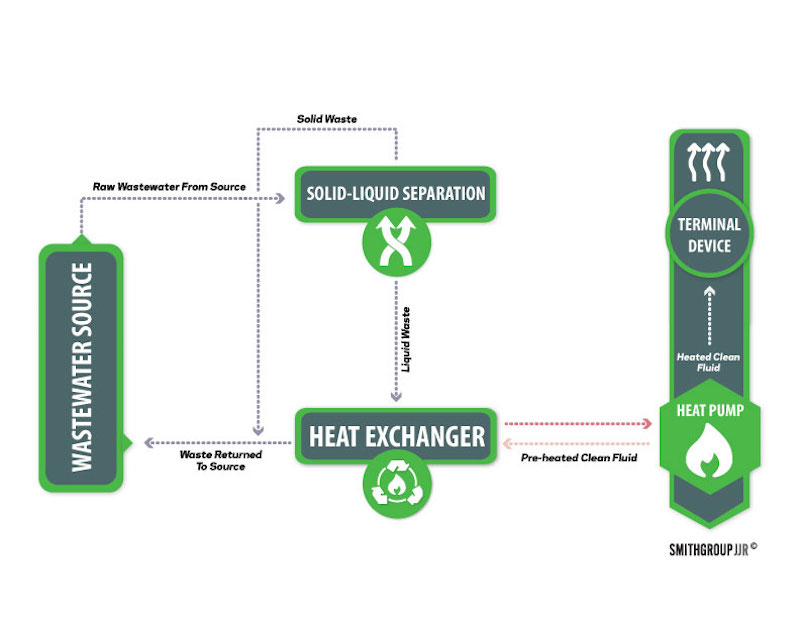

The sewer piping infrastructure already existing on site for the new DC Water headquarters could not be cost-effectively replaced or retrofitted to accommodate an in-line system. However, there already was a large wet well at the O Street Pump Station that could be incorporated into an off-line system. From that point, we focused our research on finding the best international manufacturers of off-line wastewater energy exchange systems.
International Wastewater Systems (IWS) was chosen for their significant commercial installations in North America, as well as ability to address local maintenance and repair services from the Washington, DC area. An added bonus: after final life cycle cost analysis, IWS’s system, called SHARC, has the highest energy efficiency, lowest yearly maintenance costs and lowest first costs of all manufacturers considered.
The next post in this series will look at the life cycle cost rationale for wastewater energy exchange systems, exploring energy cost savings, operational cost differences and how these all build the business case for tapping into the stream of energy that right now flows unnoticed and unappreciated right beneath our feet.
More from Author
SmithGroup | Mar 28, 2023
Inclusive design requires relearning how we read space
Pulling from his experience during a campus design workshop, David Johnson, AIA, LEED AP, encourages architects to better understand how to design spaces that are inclusive for everyone.
SmithGroup | Feb 27, 2023
Surfing the Metaversity: The future of online learning?
SmithGroup's tour of the Metaversity gives us insight on bringing together physical and virtual campuses to create a cohesive institution.
SmithGroup | Nov 28, 2022
Data centers are a hot market—don't waste the heat!
SmithGroup's Brian Rener shares a few ways to integrate data centers in mixed-use sites, utilizing waste heat to optimize the energy demands of the buildings.
SmithGroup | Aug 3, 2022
Designing learning environments to support the future of equitable health care
While the shortage of rural health care practitioners was a concern before the COVID-19 pandemic, the public health crisis has highlighted the importance of health equity in the United States and the desperate need for practitioners help meet the needs of patients in vulnerable rural communities.
SmithGroup | Aug 10, 2021
Retail reset: The future of shopping malls
Developers and design partners are coming together to reimagine how malls can create a new generation of mixed-use opportunities.
SmithGroup | May 17, 2021
Future pandemic preparedness at the medical district scale
The current COVID-19 pandemic highlights the concern that we will see more emergency events in the coming years.
SmithGroup | Jan 25, 2021
Amid pandemic, college students value on-campus experience
All the students we interviewed were glad that they returned to campus in one form or another.
SmithGroup | Aug 13, 2020
Renewing the healing role of public parks
While we can’t accurately predict all the ways we will respond to the current COVID-19 pandemic, it should provide a moment of reflection as we see all too clearly the consequences of our exploitation and destruction of nature.
SmithGroup | Jul 21, 2020
How design of senior living communities must change after COVID-19
The cost of maintaining high quality of care and high quality of life for senior living communities has increased up to 73% for senior living communities that remain free of COVID-19 and up to 103% for COVID-19 positive senior living communities.
SmithGroup | Jun 12, 2020
How will museums change after COVID-19
This new environment may herald innovative economic models and change the way we think about museum design.
















